Statistics
Mean, standard deviation
# Throw a laplace dice 10000 times. Calculate mean
# and corrected standard deviation of this sample.
use math: sqrt
function mean(a)
return a.sum()/len(a)
end
function sigma(a,m=null)
if m is null
m = mean(a)
end
return sqrt(a.sum(|x| (x-m)^2)/(len(a)-1))
end
Stat = table{
function string()
return """\
mean = {:f4},\n\
sigma = {:f4}\
""" % [self.mean, self.sigma]
end
}
function stat(a)
m = mean(a)
return table Stat{mean = m, sigma = sigma(a,m)}
end
s = stat(rng(1..6).list(10000))
print(s)
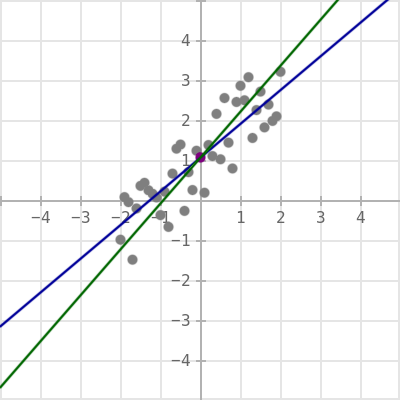
Simple linear regression
LinearRegression = table{
function string()
return """\
center = [mx,my]
mx = {mx:f4}
my = {my:f4}
rxy = {rxy:f4}
y(x) = ax*x+bx
ax = {ax:f4}
bx = {bx:f4}
x(y) = ay*y+by
ay = {ay:f4}
by = {by:f4}
""" % record(self)
end
}
function linear_regression(a)
vx,vy = list(zip(*a))
mx = mean(vx)
my = mean(vy)
sx = vx.sum(|x| (x-mx)^2)
sy = vy.sum(|y| (y-my)^2)
sxy = a.sum(|[x,y]| (x-mx)*(y-my))
ax = sxy/sx; bx = my-ax*mx
ay = sxy/sy; by = mx-ay*my
return table LinearRegression{
rxy = sxy/sqrt(sx*sy),
center = [mx,my],
mx = mx, my = my,
ax = ax, bx = bx,
ay = ay, by = by,
fx = |x| ax*x+bx,
fy = |y| ay*y+by,
gx = |y| (y-bx)/ax,
gy = |x| (x-by)/ay
}
end
rand = rng()
a = list(-2..2: 0.1).map(|x| [x,x+2*rand()])
r = linear_regression(a)
print(r)
# Let us plot this sample
use plotlib: system
s = system(w=400,h=400,count=5)
s.scatter(a,color=[0.5,0.5,0.5])
s.scatter([r.center],color=[0.5,0,0.5])
s.flush()
s.plot([r.fx,r.gy])
s.idle()
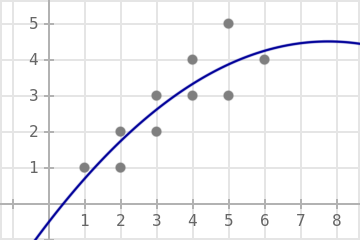
Simple polynomial regression
# The least squares method applied to a polynomial function of
# degree n leads to a linear equation system of n+1 equations.
use math.la: vector, matrix
use math.la.inversion: solve
function regression(points,{degree})
n = degree
A = matrix(*(
list(points.sum(|[x,y]| x^(i+j)) for j in 0..n)
for i in 0..n))
w = vector(*(points.sum(|[x,y]| y*x^i) for i in 0..n))
a = solve(A,w)
return table{coeff = a, f = |x| (0..n).sum(|k| a[k]*x^k)}
end
use plotlib: system
points = [
[1,1],[2,1],[2,2],[3,2],[3,3],
[4,3],[4,4],[5,3],[5,5],[6,4]
]
s = system(w=360,h=240,count=5,align=["left","bottom"])
s.scatter(points,color=[0.5,0.5,0.5])
t = regression(points,degree=2)
s.plot(t.f)
s.idle()
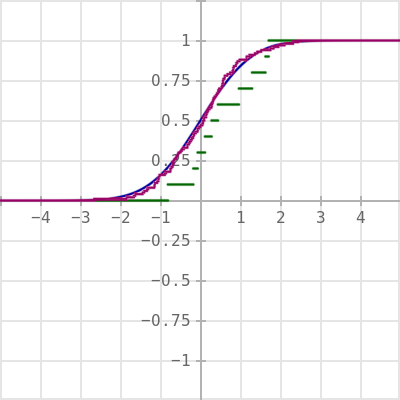
use math: sqrt,erf
use plotlib: system
# Numerical analysis:
# inversion by bisection method
use math.na: inv
# Inverse transform sampling
function rng_cdf(F)
rand = rng()
return || inv(F,rand(),-100,100)
end
# Take a list of random numbers and return the
# cumulative distribution function of this sample.
function cdf(a)
return |x| a.count(|X| X<=x)/len(a)
end
# CDF: normal distribution
function norm({mu,sigma})
return |x| 0.5+0.5*erf((x-mu)/sqrt(2*sigma^2))
end
# CDF: standard normal distribution
Phi = norm(mu=0,sigma=1)
X = rng_cdf(Phi)
F1 = cdf(X.list(10))
F2 = cdf(X.list(100))
s = system(w=400,h=400,count=5,scale=[1,0.25])
s.plot([Phi,F1,F2])
s.idle()
Obtaining a CDF from a PMF
use math: pi, exp, sqrt
use math.na: pli, integral
# Optionally, cache the values by
# piecewise linear interpolation.
function cache(f,a,b,d)
return pli(a,d,list(a..b: d).map(f))
end
erf = |x| 2/sqrt(pi)*integral(0,x,|t| exp(-t^2))
erf = cache(erf,-100,100,0.01)