| ↑ Up |
# Iterative
fac = fn|n|
y = 1
for i in 1..n
y = y*i
end
return y
end
# Recursive
fac = |n| 1 if n==0 else n*fac(n-1)
# Functional
fac = |n| (1..n).reduce(1,|x,y| x*y)
# As a dynamic system
Fac = |[n,y]| [n+1,y*(n+1)]
fac = |n| (Fac^n)([0,1])[1]
fac = |n| Fac.orbit([0,1]).skip(n)()[1]
# Tail-recursive
function call(f,n,y)
x = f(n,y)
while x: Function
x = x()
end
return x
end
Fac = |n,y| y if n==0 else || Fac(n-1,y*n)
fac = |n| call(Fac,n,1)
# Recursive, by Y combinator
Y = |F| (|x| x(x))(|x| F(|n| x(x)(n)))
fac = Y(|f||n| 1 if n==0 else n*f(n-1))
# Corecursive
fac = |n| fn*||
y=1; k=1
while true
yield y
y, k = y*k, k+1
end
end.skip(n)()
# By counting all permutations inside of the
# space of all mappings from 0..n-1 to 0..n-1
fac = |n| (list(n)^n).count(|t| (0..n-1).all(|x| x in t))
# By generating all permutations and counting them
use itertools: permutations
fac = |n| permutations(n).count()
# Print them to the terminal
(0..9).map(|n| [n,fac(n)]).each(print)
# Generate all permutations of a list
function permutations(a)
if len(a)<=1
return [copy(a)]
else
b = []
x = a[..0]
for p in permutations(a[1..])
for i in 0..len(a)-1
b.push(p[..i-1]+x+p[i..])
end
end
return b
end
end
# Return an interator instead of a list
function permutations(a)
return fn*||
if len(a)<=1
yield copy(a)
else
x = a[..0]
for p in permutations(a[1..])
for i in 0..len(a)-1
yield p[..i-1]+x+p[i..]
end
end
end
end
end
for n in 0..4
permutations(list(n)).each(print)
end
# Generate all permutations of an ordered
# list in lexicographical order
function permutations(a)
if len(a)==0
return [[]]
else
b = []
for i in 0..len(a)-1
for x in permutations(a[..i-1]+a[i+1..])
b.push([a[i]]+x)
end
end
return b
end
end
# Return an iterator instead of a list
function permutations(a)
return fn*||
if len(a)==0
yield []
else
for i in 0..len(a)-1
for x in permutations(a[..i-1]+a[i+1..])
yield [a[i]]+x
end
end
end
end
end
# Take any iterable
perm = |a| permutations(list(a))
# Generate all k-permutations of an ordered # list in lexicographical order perm = |a,k=len(a)| [[]] if k==0 else list([a[i]]+x for i in len(a) for x in perm(a[..i-1]+a[i+1..],k-1))
# as a list
prod = |*a| [[]] if a==[] else list(
[x]+t for x in a[0] for t in prod(*a[1..]))
# as a set
prod = |*a| {[]} if a==[] else set(
[x]+t for x in a[0] for t in prod(*a[1..]))
# as an iterator
prod = |*a| iter([[]]) if a==[] else (
[x]+t for x in a[0] for t in prod(*a[1..]))
# as a list
prod = |*a| a.reduce([[]],|x,y| (x*list(y)).map(|[t,s]| t+[s]))
There is a recursive formula for the Bernoulli numbers:
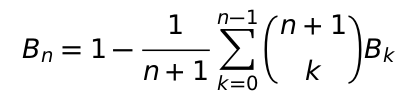
This formula can be implemented directly, taking advantage of exact rational numbers in combination with long integers.
# memoizing fixed point combinator
use functional: fix
# rational numbers
use math.rational: rat
# binomial coefficient
use math.cf: bc
B = fix({},|B,n| 1 if n==0 else
1-rat(1,n+1)*(0..n-1).sum(|k| B(k)*bc(n+1,k)))
for n in 0..8
print([n,B(n)])
end
# [0, 1]
# [1, 1/2]
# [2, 1/6]
# [3, 0]
# [4, -1/30]
# [5, 0]
# [6, 1/42]
# [7, 0]
# [8, -1/30]
print(B(60))
# -1215233140483755572040304994079820246041491/56786730
Alternatively:
# factorial, # Eulerian numbers of the first order, # Stirling numbers of the second kind use math.cf: fac, euler1, stirling2 B = |n| rat( n*(0..n-1).sum(|k| (-1)^k*euler1(n-1,k)), 2^n*(2^n-1) ) B = |n| (0..n).sum(|k| rat((-1)^k*fac(k)*stirling2(n+1,k+1),k+1)) B = |n| rat(1,2) if n==1 else (0..n).sum(|k| rat((-1)^k*fac(k)*stirling2(n,k),k+1)) B = |n| rat(n,2^(n+1)-2)*(0..n-1).sum(|k| rat(fac(k)*stirling2(n,k+1),(-2)^k))